ISO 9001 Internal Audit Status Report Template
Internal audits play a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness and compliance of a quality management system. They provide an opportunity for organizations to identify areas of improvement and address any non-conformances. As part of the ISO 9001 certification process, organizations must conduct internal audits and report on their findings.
Understanding the Importance of Internal Audits in ISO 9001
Internal audits are critical for organizations to ensure compliance with ISO 9001 standards. By conducting regular and systematic reviews of their quality management system, companies can identify potential issues, non-conformances, and areas for improvement. This helps them maintain the highest level of quality and customer satisfaction.
Internal audits also allow organizations to assess their processes, procedures, and controls, ensuring they align with ISO 9001 requirements. This comprehensive evaluation helps businesses identify and mitigate risks, enhance efficiency, and drive continuous improvement.
In addition, internal audits play a vital role in demonstrating an organization's commitment to quality management and their adherence to ISO 9001 standards. By evaluating the effectiveness of their quality management systems through internal audits, companies can establish trust and credibility with stakeholders, including customers, regulators, and partners. Ultimately, this can increase customer satisfaction and improve operational performance and competitive advantage.
In the next section, we will dive deeper into the key components of an internal audit status report in ISO 9001. We will explore how to effectively prepare and present this report, ensuring it provides valuable insights for driving organizational improvement. Stay tuned as we uncover the essential elements and best practices for creating an informative and impactful internal audit status report.
The Key Components of Internal Audit Status Report In ISO 9001
The Internal Audit Status Report in ISO 9001 serves as a crucial document for tracking and communicating the progress of internal audit projects. The key components outlined in the report contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the project's status and facilitate effective communication between the audit team and stakeholders. Let's expand on each of these components:
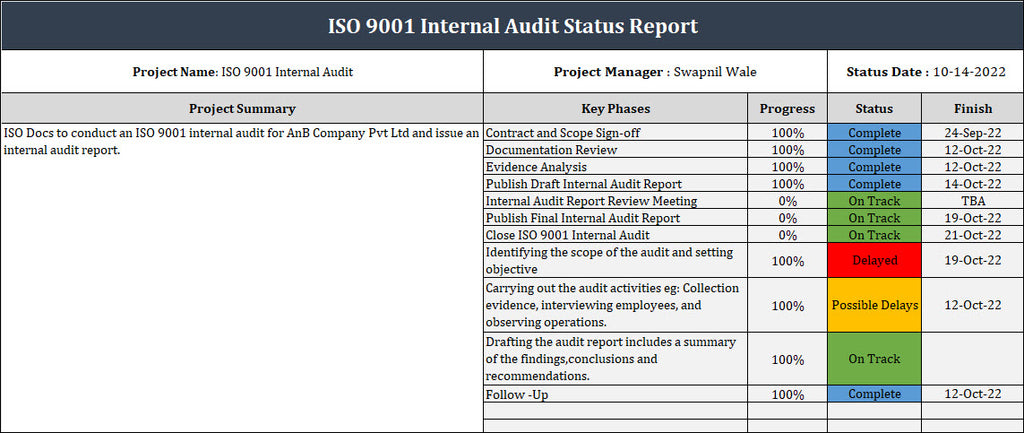
1. Project Summary: The project summary is a snapshot of the internal audit, briefly outlining its objectives, scope, and importance. It serves as an introduction for stakeholders who may not be intimately familiar with the project, providing context and establishing the overall purpose.
2. Key Phases: This section delves into the various phases of the internal audit, emphasizing planning, execution, and reporting. Stakeholders gain insights into the project's lifecycle by highlighting progress and potential deviations from the original plan. This information aids in understanding where the project stands and what to expect in subsequent phases.
3. Status: Providing an overall status update, this section informs stakeholders whether the internal audit project is on schedule, facing delays, or encountering challenges. Clear and concise status updates enable stakeholders to gauge the project's health and make informed decisions.
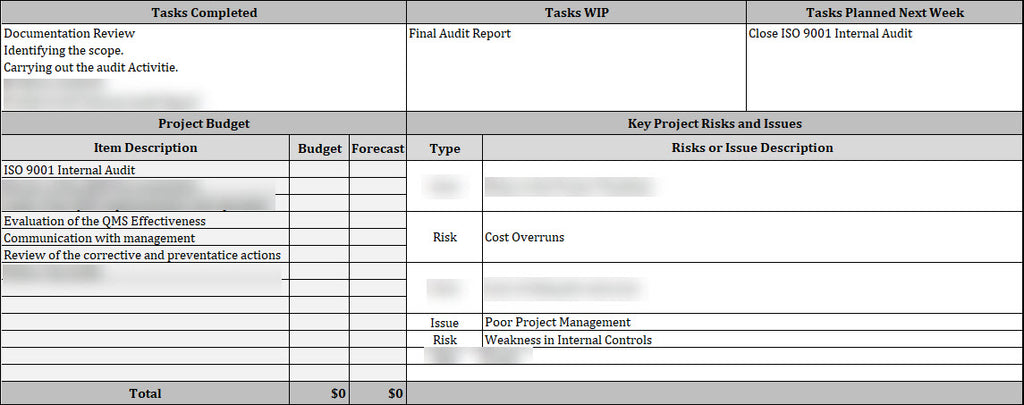
4. Tasks Completed: Listing completed tasks since the last report, this section showcases tangible progress. Activities such as interviews, evidence gathering, data analysis, and developing audit findings are documented, demonstrating the team's accomplishments and contributions to the audit process.
5. Tasks WIP (Work in Progress): Highlighting ongoing tasks, this section offers insight into the current focus of the audit team. Information on estimated completion dates and any challenges faced gives stakeholders a real-time view of the project's dynamics.
6. Tasks Planned Next Week: This forward-looking section outlines upcoming tasks scheduled for completion in the following week. It serves as a roadmap for stakeholders, offering a glimpse into the project's future direction and anticipated activities.
7. Project Budget: Providing financial transparency, this section details the allocated budget for the internal audit project. It includes information on expenses incurred to date and any changes in the budget. This ensures that stakeholders are aware of the financial aspects of the project and can make informed decisions.
8. Key Project Risk Issues: Identifying and describing significant risks or issues, this section includes a risk assessment and mitigation plan. By proactively addressing potential challenges, the audit team minimizes negative impacts and ensures a more prosperous and smooth completion of the internal audit.
Analysing Audit Results and Identifying Areas For Improvement
Once the internal audit has been conducted and the audit findings have been documented, the next step is to analyze the results and identify areas for improvement. This is a crucial part of the internal audit process as it provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of the organization's quality management system and highlights areas that need attention.
When analysing the audit findings, it is essential to categorize them based on their severity and impact on the organization's ability to comply with ISO 9001 requirements. This allows for prioritization of corrective actions and allocation of resources to address the most critical issues first.
In addition to identifying areas for improvement, it is also important to consider the root causes of any non-conformances or deficiencies. This enables the organization to implement corrective actions addressing the underlying issues rather than treating the symptoms.
Furthermore, it is beneficial to involve relevant stakeholders in the analysis process. This ensures that different perspectives and expertise are considered, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of the audit results and generating buy-in for any necessary changes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, analysing the audit findings and identifying areas for improvement is a critical step in the internal audit process of ISO 9001. Organizations can prioritise corrective actions and allocate resources efficiently by categorizing the findings based on severity and impact. Understanding the root causes of non-conformances or deficiencies allows for implementing practical corrective actions that address underlying issues. It is essential to involve relevant stakeholders in the analysis process to gain different perspectives and generate buy-in for necessary changes.
