ISO 27001 Management Review Agenda Template
Introduction
So you’re working with ISO 27001 and you know about the management review meeting. It’s a key part of the standard specifically Clause 9.3 but it’s more than just another box to tick. Think of it as your organisation’s chance to step back, look at how your Information Security Management System (ISMS) is performing and make sure it’s still doing what it’s supposed to do. Is it effective? Does it meet your company’s objectives? Are there risks creeping in that need to be addressed?
A good management review agenda keeps these meetings on track. It ensures you’re hitting all the points ISO 27001 expects—without wasting anyone’s time or missing something critical.
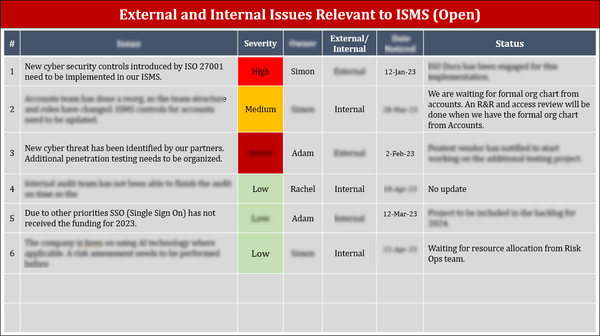
Why ISO 27001 Management Review Template Is Non-Negotiable?
It is always dangerous to have the management review as a last box to tick before your audit. ISO 27001 Clause 9.3 is not just bureaucracy; it is the mechanism whereby information security is raised as a strategic priority and made relevant into the future-and indeed has the potential to be transformative. Organizations treating ISMS as an offside or ancillary activity often do badly-since these reviews (or I'd rather call these appraisal meetings) are the points where leadership meets execution. Here are some reasons as to why this process is important:
- It Is Mandatory
Clause 9.3 mandates that the ISMS be reviewed by top management at planned intervals, covering performance, audit outcomes, trends in risk, and opportunities for improvement. Neglect any of these topics, or do not write them down, and the auditors can issue nonconformities at will.
- Attracts the Participation of Leadership
Senior leaders-from CISO to Finance, HR, Legal-must actively participate. This shows leadership commitment (Clause 5.1), what is critical to align ISMS objectives with organizational strategy.
- It Builds an Audit Trail
Having agendas, attendance lists, minutes, decisions, and action-tracking on hand provides robust evidence that your ISMS is operational and evolving .
- Triggers Continuous Improvement
The review is where you analyze trends—incident frequency, audit findings, KPI gaps—and decide on corrective and preventive actions.
- Keep the ISMS Alive and Relevant
The ISMS will become more stale without further oversight. These meetings keep controls and policies aligned as the business evolves, risks change, or regulators' landscapes shift.
- Aligns Security with Strategic Goals
These reviews are the mechanisms by which ISMS objectives are linked to business strategy, not just affirming security as another cost of doing business-."
- Demonstrates Culture and Leadership Tone
Visible participation from top management shows that security matters. It sets a tone that cascades through the organization and boosts accountability.
- Strengthens Resource Allocation
It lets management see directly whether personnel, technology, or budget is sufficient for the ISMS.
- Enhances Stakeholder Confidence
In reviewing internal processes, stakeholder and public audits reassure clients, partners, and regulators-of the continued governing. Measuring and improving the overall ISMS.
Why ISO 27001 Management Reviews Matter
Management reviews Meeting are where the leadership meets the information: Where C‑Suite executives, department heads, and security practitioners evaluate ISMS performance, resource needs, and potential areas of improvement. Here is why that is important:
-
Ensures Leadership Engagement: It is human nature to deprioritize what isn’t seen. A structured review places security metrics and risk discussions in front of a decision‑maker, thereby ensuring the ISMS does not run under a separate closed door.
-
Verifies Clause 9.3 compliance: ISO 27001 specifies certain inputs (audit results, risk status, incident trends, etc.) and outputs (resource decisions, action items, changes to ISMS). If any of these are omitted, a nonconformity may be raised during certification or surveillance audits.
-
Promotes Continuous Improvement: It involves looking at performance trends — incident volumes, audit findings, objective achievements — and spotting patterns early. Whatever seems trivial can be corrected before it becomes a major failure.
-
Creates a Clear Audit Trail: Auditors want evidence that management reviews were carried out regularly, that required issues were discussed, and that documented decisions arose. A consistent agenda and good meeting minutes cover all of these aspects.
-
Aligns ISMS with Business Targets: Security is not a business in isolation. By discussing ISMS performance against business changes—mergers, new regulations, market shifts—you keep security posture aligned with strategic objectives.
- Enhances Risk Management: Jointly reviewing the risk register, the status of treatment, and emerging threats ensures a shared understanding of organizational risk appetite, which in turn improves the quality and transparency of risk decisions.
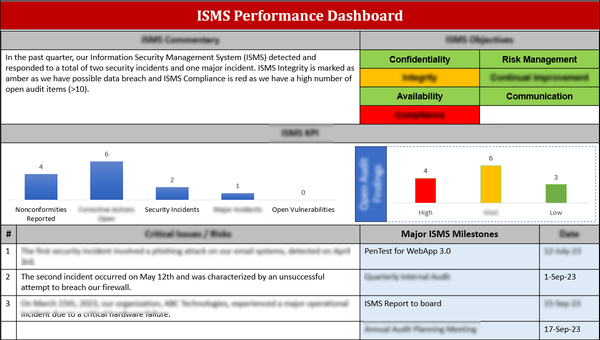
What to Include in Your ISO 27001 Management Review Agenda
Now let’s get to what actually goes into a good agenda. This doesn’t have to be a 12 page document—but it does need to cover the core points ISO requires. A well structured agenda ensures nothing gets missed and everyone is on the same page.
Here are the key items your management review should include:
- Follow-up on Previous Actions
Before you get into new topics review what came out of the last meeting. Did people do what they committed to? If not, what’s the holdup?
- Updates on Internal and External Changes
Has anything changed in the business, the legal landscape or the threat environment? Maybe you’ve taken on new customers, changed vendors or adopted cloud tools. These changes might impact your risks—or even your ISMS scope.
- Stakeholder Feedback
Customers, auditors, partners what are they saying? Did someone raise a concern or highlight a gap? Take those seriously.
- ISMS Performance
Now for the good stuff. Share performance indicators:
-
-
Are incidents decreasing?
-
Did internal audits go well?
-
Are awareness campaigns working?
-
Are security objectives on track?
-
It’s not just about the data—it’s what the data is telling you.
- Risk Assessment and Treatment Updates
What’s the current risk landscape? Are treatment plans on track? Are there new or emerging risks that need attention? Flag high-risk areas and discuss.
- Opportunities for Improvement and Resource Decisions
Wrap up by discussing what can be done better. That might mean new tools, training, policy changes or even updating the ISMS scope. And don’t forget: if decisions are made, document who’s responsible for what and by when.
Pro tip: keep your agenda the same from meeting to meeting. That way your management reviews become a rhythm not a scramble.
Management Review Without the Stress
Preparation is key to a productive review or a wasted hour.
Here’s how to prepare:
-
Plan Ahead: Schedule your review well in advance. Quarterly reviews are ideal—don’t wait for year-end chaos. Put it on the calendar and treat it like the high-priority meeting it is.
-
Get the Right People Involved: Invite stakeholders who can actually speak to the agenda topics—think CISO, risk manager, HR, IT, compliance, and legal. Top management should always be represented.
-
Send Out Pre-Reads: A few days before the meeting, share the agenda and supporting documents:
-
Incident reports
-
KPI dashboards
-
Audit results
-
Risk register updates
-
This gives everyone time to prepare so the meeting isn’t just a reading session.
-
Assign Roles
Have someone chair the meeting (usually the CISO or another senior leader), someone take minutes and others present on specific agenda items. Assigning roles ahead of time prevents awkward silences and keeps things moving.
-
Use a Consistent Format
Stick to the same agenda structure for every meeting. It helps with tracking progress and builds confidence with auditors.
-
Run the Meeting and Document It Like a ProNow it’s meeting time. Here’s how to run it and capture the important bits.
-
Stick to the Agenda
Time is short so stay on track. If a topic sparks debate, note it and assign a follow-up outside the meeting.
-
Encourage Real Discussion
This isn’t a status update—it’s a strategic review. Ask questions. Challenge assumptions. Make sure leadership is engaged and not just nodding along.
Capture It All
Document:
-
-
Who was there
-
What was discussed
-
What decisions were made
-
What actions were assigned (to whom)
-
Use plain language. If you agreed to buy a new tool or update a policy, write that down.
Avoid These Common Mistakes That Derail Reviews
The most common errors in performing reviews
Even learned teams will make the mistake of falling into these traps. For example:
-
Skips mandatory input-outputs: ISO 27001 prescripts mandatory input-output for Clause 9.3. If all requirements are not covered, then you are failing to comply.
-
Lack of documentation: From the auditor's perspective, the meeting did not happen if it was not minuted.
-
Lack of action: Repeating the same items for action in meeting after meeting serves as a signal for concern.
-
Involvement of the wrong people: You require decision-makers and experts to be involved, not just optional participation.
-
Checkbox-style activity: Do not make the reviews a simple formality; management reviews are where true change can begin.
Stay alert; see every review as an effort toward improvement and not merely an ISO 27001 requirement.
Using the Review Process to Increase Audit Readiness
If ISO 27001 certification or surveillance audit is looming over your head, among the first records auditors will want to see are management review records.
They will look for:
-
Confirm any required supporting documentation to verify the meeting took place
-
Submit the calendar appointments and the meeting logs that show all necessary participants attended the meeting.
-
A defined, complete agenda: Ensure your agenda captures all elements listed in Clause 9.3 of the standard including but not limited to: performance evaluation, relevant internal/external issues, results from the audit, and the status of corrective actions.
-
Comprehensive minutes and subsequent actions
-
The meeting minutes should capture the entire discussion but more importantly, detail each decision made and who would implement the decision within what time frame.
-
Demonstrate proactive ISMS change along with continued improvement within the organization
-
Document changes made to processes, resource requirements such as personnel, budget, and changes to risk levels illustrating an ISMS that is dynamic and constantly improving.
Then bonus points if you show the progress of the reviewed action plan, such as updated metrics, closed action plan items, improved KPI. This says your ISMS is transforming rather than just surviving.
Management reviews carried out correctly, adequately recorded, and held consistently will ensure a smooth audit period. No scrambling, no vague answers, just a practiced and confident handover.
Incorporating Management Review Outputs into the Strategy Formulation Process
Management reviews shouldn't stop at the meeting but should have feeds to the wider strategy and roadmaps. After recording decisions, action items, and resource requests, it is now time to ask, "How will this shape our next quarter (or year)?"
For instance, if you find a spike in phishing incidents from your review, then a specific awareness campaign will be rolled into your corporate training calendar. If wait times associated with risk-treatment controls for some critical system are lagging behind, you will bump that particular budget request in the next IT investment plan. And if you uncover process inefficiencies, say slow closure times for incidents, improve those as part of your digital transformation or operational excellence initiatives.
By linking review outputs to enterprise planning cycles, one would ensure security is not put in a box but becomes part and parcel of a bona fide organization performance, resilience, and innovation driver. This not only strengthens buy-in from the C-suite but also demonstrates to auditors that your ISMS lives and breathes and is fully embedded in strategy planning.
Conclusion
An ISO 27001 management review agenda template may appear to be a simple tool, but the real value comes into play when the template is put into action. This helps ensure your ISMS stays on track with your goals, keeps management informed, and helps you prepare for the audit process. Whether you are at his nascent stage of ISO 27001 implementation or have been certified for years, a structured and deliberate management review process can give you the edge.

