ISO 27001 Internal Audit Status Report Template Download
Overview
ISO 27001 internal audit status report meant for the Information Security Management System (ISMS) is a formal document to summarize the results of internal audits. The report provides information to management on the status of the audits clearly regarding compliance with ISO 27001 requirements. It will normally contain the key findings, corrective actions, and status updates. In this respect, as an Internal Audit Status Report Template is generally used in practice, it also allows consistent reporting. The template enables auditors to record the objectives, scope, and outcomes for each audit cycle. By utilizing such a template or an audit findings tracking template, teams can be able to streamline reporting, save valuable time, and bring out key information. According to ISO 27001, internal audit results must be documented and reported to management as part of the organization's records. A good status report will thus evaluate controls and risks, follow up on evidence, summarize findings, and recommend actions. The internal audit status report is beyond the realm of formality; it is a strategic outlook of your security posture.
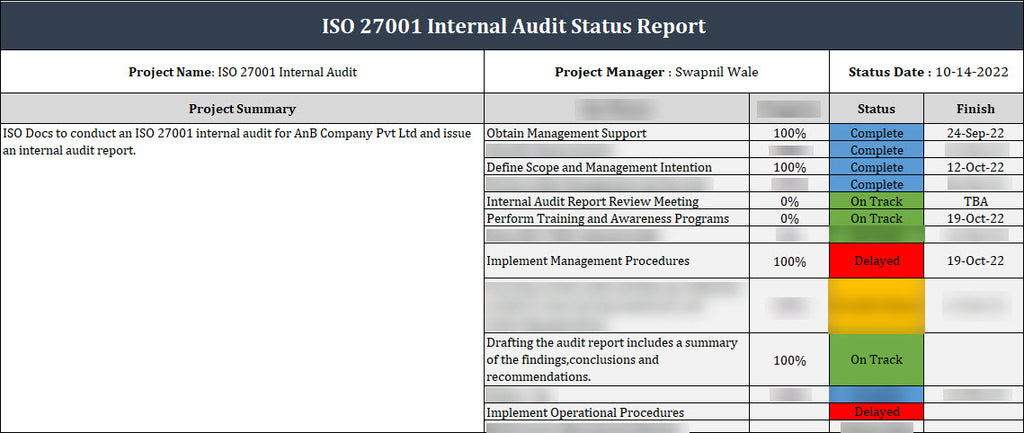
Important Aspects Of An Internal Audit Status Report
A well-laid-out internal audit status report relies on predetermined contents. These generally include the following main sections and elements (as supported by best practices around the world).
- Executive Summary: A high-level overview of audit results and audit status. This summarizes the main findings, compliance status, and immediate action items for quick review by management.
- Scope and Objectives: Describes what was audited and why. It includes audit scope, date range for the audit, and statement of objectives. For example, state which ISO 27001 clauses or business units it covered. ISO guidance says you need to set clear audit objectives at the start.
- Audit Schedule and Team: An audit timing and personnel publication. The template should list planned audit dates or timeline and the members of the audit team, with defined roles. Including an audit schedule will provide evidence for tracking planned vs. actual progress.
- Methodology: A brief description of the audit methods (interviews, document review, testing). How evidence was gathered together with a check on control. In other words, describes the basic steps followed during the audit, as well as the sampling procedures employed.
- Findings: The core content of the report. Each finding (conformity or non-conformity) should be described, often following the mapping of the specific ISO clause or control it relates to. The report should include details about positive findings (where controls are working) and findings about issues (gaps or non-conformities). Usually there will also be evidence and an impact assessment accompanying every found non-conformance.
- Recommendations/Corrective Actions: For every issue identified, there should be recommended actions in the report. This section outlines what to change, who to change, and by when. An action plan to fix the non-conformity is also often contained in this section.
- Appendices/Evidence: Supporting appendices or evidence. Any key evidence (screenshots, logs, test results) can be attached or referenced. This makes sure that there is a documented audit trail without congesting the main report with evidence.
- Audit Objectives: Goal(s) formed for the audit in clear terms (e.g., "Verify compliance of ISO 27001 A.9 on access control").
- Audit Team: Names and roles of the auditors. This shows independence and qualification, which ISO 27001 requires auditors to be impartial.
- Timeline & Milestones: Start/end dates and key milestones (e.g., draft report due, review meeting). This helps stakeholders keep abreast of when results will be available.
- Key Risks/Issues: A summary of major risks or issues identified during the audit to attract the attention of management. (Some templates list key risks and issues to highlight any critical vulnerabilities that surfaced.)
-
Status Indicators: Clear status markers (e.g., Completed, In Progress, Outstanding) should be applied to resource tasks or actions. They may be referenced in color or a tabular form in the report for visual progress checks.
The overall intention of these components is clarity and completeness. An effective audit report is, as one blog states, a living blueprint for growth if it brings together findings with controls and evidence.
What Are The Benefits Of Using A Template For A Status Report?
Templates, especially a standardized Internal Audit Status Report Template, ensure many advantages.
- Consistency and Completeness: Each audit report prepared with the aid of a template contains all sections required. Auditors cannot forget verifying the inclusion of objectives, scope, or findings. Such consistency mirrors Annex A of ISO 27001, Clause 9.2, which states that audits must be documented as part of the audit program.
- Improved Governance: According to a toolkit description, the internal audit status report “improves reporting and enhances governance.” Practical application finds management receiving organized information within acceptable time limits, thus making the local governance of security initiatives much easier.
- Efficiency: Filling in a pre-formatted document cuts time for the auditors instead of creating reports from scratch. The template usually constitutes placeholders and prompts like a table for findings that speed up documentation.
- Tracking of Actions: Integrated with the audit findings tracking template, the status report automatically connects findings to corrective actions which indicates overdue and completed actions.
- Audit Trail: Templated recording of every audit cycle. It can be stored as proof of compliance during ISO certification or any regulatory reviews since ISO 27001 requires maintaining audit results.
- Communication: When well formatted, the report becomes easy for the stakeholders (management, board, regulators) to review. Summaries, tables, and highlighting ensure easy communication of the ISMS status.
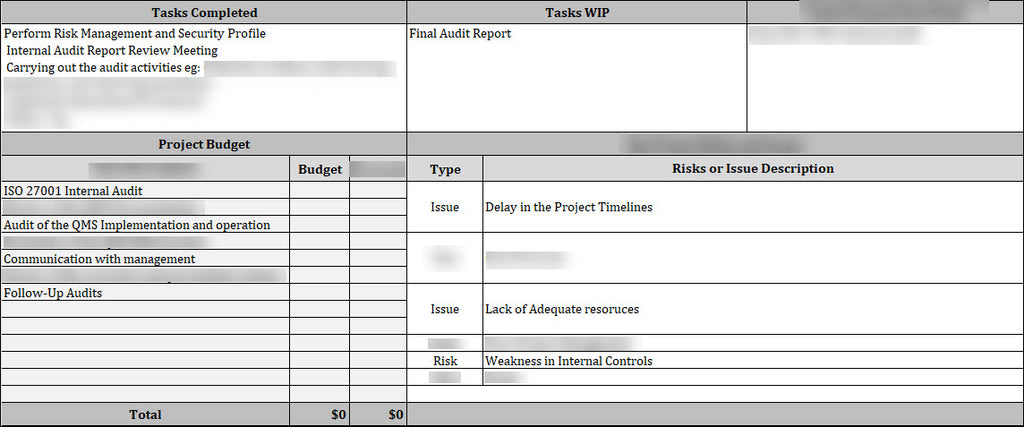
Tracking Audit Findings With A Template
This includes an extremely important part of the process of internal audit report-making whereby issues picked are tracked. A template for tracking the audit observations (usually an Excel spreadsheet or other database) is used along with the status report to enter and document each observation and its subsequent closing. The audit findings tracking template allows the teams to track each issue from identification through to closure. The necessity of documenting findings is outlined in the ISO 27001 guidance: “Auditors should record the findings during each audit. This includes both positive aspects (conformities) and areas needing improvement (non-Conformities)”. Each finding must then initiate corrective action. Specialists say that for every major non-conformity there should be “an explicit corrective action, an owner, and a close date”. The tracking template achieves this by requesting the name of the owner and the deadline.
For example, if the audit finds that a gap exists in the firewall rule (i.e., a nonconformity), that gap would be entered into the finding tracker against the identified control (possibly A.12.4.1 Logging), with the network team assigned as the owner of the action to update the rule and a date assigned for when it must be done. Once the action has been assigned, progress could be noted in status (open/pending with options for filter color code for overdue). Thus, this continuing tracking should ensure that no finding is lost and that each will be followed until finally changed to closed satisfactorily by verification.
Keeping up and running a log of audit findings is important for further improvement, giving top management visibility on how long it takes to close issues raised. These guidelines suggest corrective actions are needed after documenting findings: “assign corrective actions… and track progress”. This means the template made for tracking will allow for easy summary generation for management (for example, how many findings are still open this month opposed to last month). All in all, it shows how the audit findings tracking template complements the status report, which provides a detailed account of the status of each finding along its lifecycle.
The basic columns usually contained in an audit findings log include:
- Finding ID/Reference: A unique number or code for each finding (e.g., “2024-A01”).
- Description: A brief statement identifying the issue or observation.
- ISO Clause/Control: The ISO 27001 clause or Annex A control specifically related to the finding.
- Finding Type: Nonconformity, Observation, Opportunity for Improvement, etc.
- Risk/Priority: An assessment of severity or risk level.
- Audit Evidence: Copies of the documents or samples reviewed (record IDs, screenshots, etc.).
- Assigned To: The person or department responsible for corrective action.
- Corrective Action: What needs to be done to correct the issue.
- Due Date: By when this corrective action needs to be completed.
- Status/Progress: The current status (Open, In Progress, Closed), and what percentage has been completed.
Creating Your Internal Audit Status Report
Some general steps are applicable when utilizing the Draft Status Report template and the Audit Findings Tracking Template:
1. Plan and Schedule the Audit: ISO 27001 says that audits should take place at predefined intervals. Therefore, you must specify the audit period and scope beforehand. You can record the starting/ending dates and expected completion schedule in the Report.
2. Audit Execution: Carry out an audit according to the audit plan. Evidence may be gathered through interviews, document analysis, and testing. You can use the internal audit checklist to make sure all relevant controls have been examined.
3. Report Findings: For each finding during the audit, record in the status report and/or findings log. Both conformities and nonconformities should be included. Ensure enough detail is provided and include evidence reference.
4. Complete the Status Report: Fill in critical information in the report template: status of tasks completed, progress made, and milestones reached. Include metrics that apply to the project or audit (e.g. the number of controls tested). Summarize major issues under section “Key Findings”.
5. Assign Corrective Actions: For each problem identified, come up with a corrective action plan. Assign responsibility and deadlines. Update the Audit Findings Tracking Template with this information. Make sure every finding has an owner and a due date.
6. Review and Approve: The management or the audit sponsor should review the draft of the status report. Review shooters and feedback, then finalize the document. Approval (signature) ensures there is accountability.
7. Track Closure of Actions: Use the template to track actions and update their status. Regularly (weekly or monthly) check for progress and report on status, indicating whether items are closed or overdue.
8. Report to Management: The final Internal Audit Status Report is presented in a management review meeting, with emphasis on those nonconformities still open and how corrective actions are proceeding. This fulfills ISO 27001 requirements for communicating audit results to top leadership.
9. Continuous Improvement: Once findings are closed, trends will be analyzed. Reoccurrence of the same issue would indicate that it is indeed systemic. Update policies or training where appropriate to improve.
Audit Reports: Best Practices for Maximizing Benefits and Minimizing Harm
Most useful tips to consider for effective presentation of the status of your audit:
- Be Clear and Concise: Write in simple language. Keep jargon to a minimum. When possible, summarize findings in bullet points or tables. An executive summary with a quick snapshot (say, counts of findings, percentage closed) helps executives “react to numbers, not stories.”
- Link Findings to Evidence: Where possible, reference the evidence that supports a finding. As ISMS online advises, each finding should be “mapped to a regulatory clause and linked evidence”. This requires proof of the finding and ease of verification.
- Focus on Actionable Insights: State implications of findings. For example, do not only say that “policy is missing”; explain why: “Without an access control policy, user privileges might be inconsistently granted.” State what needs to change and who needs to change it.
- Prioritize Findings: Urgency is displayed by risk ratings or categories. Flag “Critical” ones in red for example. One expert suggests not just labelling them non-conformities, but also “issue criticality and impact”. This will allow management to focus on the highest risks.
- Use a Standardized Format: Always abide by an agreed format or template so that the readers will at least know where to look. Use headings, numbered lists, and consistent numbering of findings, e.g. N1, N2.
- Use Charts, Diagrams, and Any Other Visuals: Any charts or graphs may be included (e.g. pie chart of open versus closed findings, or a heatmap of risk areas) for illustration. A picture tells the story of the status of the audit cycle: a few seconds of glancing and anybody is fully updated.
- Always Bring the Response Back: Ensure that actions assigned are verified. Update the report with closure dates and evidence of fixes. The postulate is that “every finding… has an owner and a close date”.
- Keep a Copy of All Reports: Maintain copies of status reports year in and year out. This archive very quickly turns into a record of continuous improvement. It is also handy in auditing the audit process itself. ISO audits will wish to see ago internal audit records.
- Optional: Custom Applications. If possible, use audit management software or dashboards. Digital solutions can automatically track findings and generate reports. They will also enforce version control and deadlines. A well-updated spreadsheet will also do just fine.
A good ISO 27001 Internal Audit Status Report implementation using such practices will change from paperwork into a tool with which to drive the ISMS forward. Ultimately, audit reporting should provide the impetus to change for the better and to more robust security.
Conclusion
An ISO 27001 Internal Audit Status Report Template is a powerful means to put on record the effectiveness of your ISMS. Given the standardized report and a complementary audit finding tracking template, it guarantees that all audit finding addresses will be recorded. It provides a handy guide for the managers to comprehend a bird's eye view of compliance, outstanding issues, and progress. Most important ISO 27001 makes it a requirement that internal audits be documented and results sent to management. A good template helps in satisfying this requirement with a lot of time saving and consistency on its side. In brief, main tasks include formulating the objectives of the audit, collection of evidence, documenting findings, and dispatching corrective actions. Monitoring each finding until its closure keeps your ISMS in line with the ISO 27001 mission of continuous improvement.

