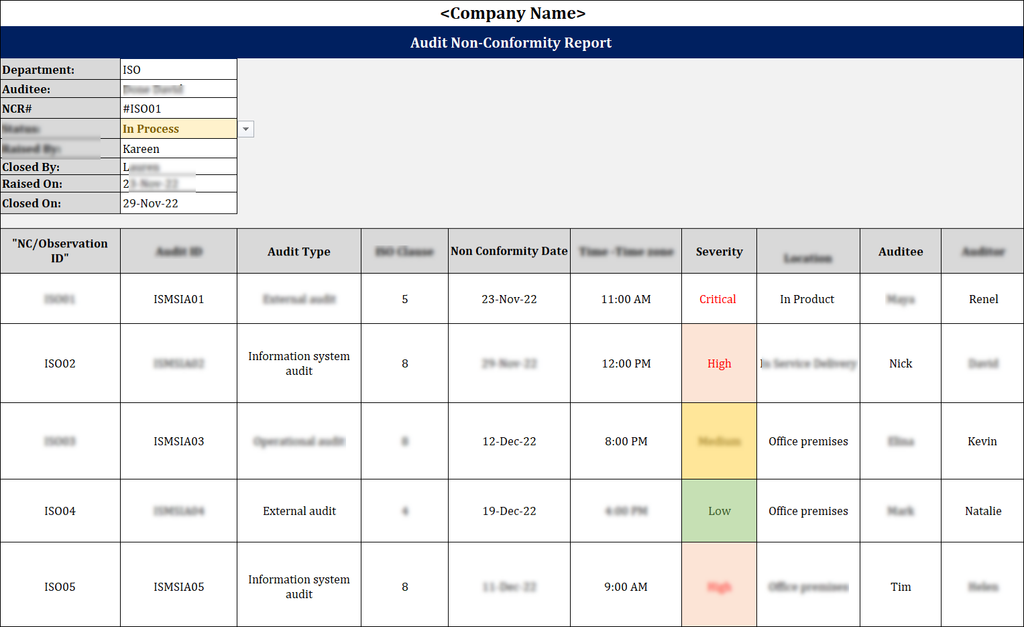
ISO 27001 Audit Non-Conformity Report Template
Overview
An ISO 27001 Audit Non-Conformity Report Template is a formal document used to record any issues found during an audit. This helps the organizations to clearly document issues, categorize their severity and assign proper actions. This helps in continual improvement by ensuring that all non-conformity are taken care of in a systemic way and within the ISO framework.
Purpose Of ISO 27001 Audit Non-Conformity Report Template
ISO 27001 Audit Non-Conformity Report Template provides a structured format for identifying, documenting, and managing deviations from ISO 27001 requirements during audits. It ensures the non-conformities are recorded with evidence, categorized and assigned corrective action. This helps the business to track and implement improvements and be compliant with the ISO 27001 standard.
Importance Of A Non-Conformity Report Template
A Non-Conformity Report Template plays an important role in documenting any issues found during a ISO 27001 audit. The template documents what went wrong, why it happened and what actions are taken to fix the issues. This way the problems are resolved without any delays. The template also helps in accountability by assigning responsibility for corrective actions. Non-Conformity Report Template supports ISO 27001 compliance and helps in continuous improvement by detecting and avoiding future incidents.
Types Of Non-Conformities
There are 4 types of non-Conformities:
1. Major Non-Conformity: A major non-conformity is a complete breakdown of the required controls. This can lead to suspension of certification if not addressed promptly. It signifies a failure to meet the ISO 27001 requirements which affects the Information Security Management System.
Examples:
- Risk assessment has not been conducted.
- No documentation of information security policies.
- Failure to conduct management reviews and inter audits.
Impact: Quick action should be taken, which affects the effectiveness of the ISMS.
2. Minor Non-Conformity: A minor non-conformity is an isolated issue which is not critical, but still requires a corrective action to maintain compliance. It does not have a major impact on the implementation of ISMS.
Examples:
- A department missing to review access logs in time .
- An outdated document is still being used.
- Minor gaps in training records.
Impact: This does not delay certification, but the issues must be addressed for total compliance.
3. Observations or Opportunities for Improvement (OFIs): These observations are not technical in nature, but need attention before they become a major issue.
Examples:
- Documents are right but need better structure for clarity.
- Logs are maintained manually, which can be automated.
Impact: Corrective action is not compulsory but taking action is helpful for the organization
4. Critical Non-Conformity: Security breaches, complete absence of controls and legal violations come under critical non-conformity. These conformities are pointed out by the auditors
Examples:
- Data breach not reported.
- No incident response in place.
Impact: This may lead to an instant suspension of certification.
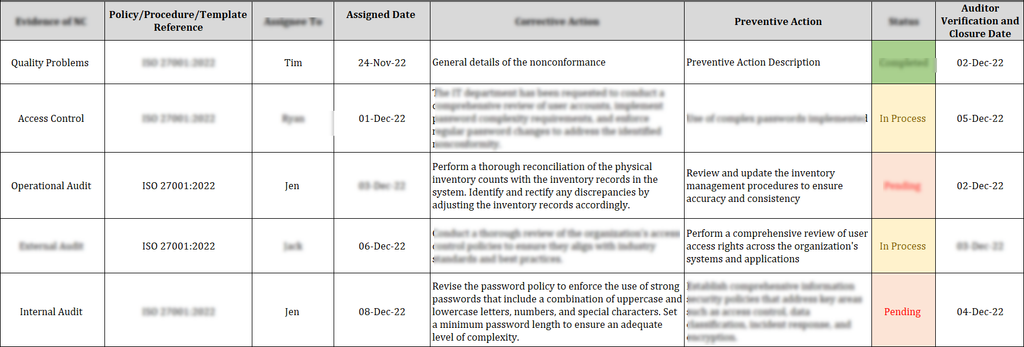
Key Elements Of An ISO 27001 Audit Non-Conformity Report Template
-
Non-Conformity Reference Number: Each non-conformity report will have a unique number to it, which helps in tracking and managing the non-conformity efficiently.
-
Audit Date and Location: To maintain a clear audit trail, recording the date and place of audit is very important.
-
Auditor Details: Name and designation details of the auditor who is responsible for identifying the non-conformity should be mentioned in the report.
-
Clause/Control Reference: ISO 27001 clause or Annex A control that maps to the non-conformity should be stated in the report.
-
Description of Non-Conformity: A detailed and clear explanation of the non-conformity should be documented in the report.
-
Root Cause Analysis: Analysing the root cause of why the issue occurred and how to prevent future re-occurrence is a must.
-
Status (Open/Closed/Pending): Tracking the progress of the non-conformity helps to make sure there is enough time for a proper closure.
Common ISO 27001 Audit Non-Conformities
Below are some of the common ISO 27001 audit non-conformities:
-
Lack of Risk Assessment: Many times, organizations miss to identify necessary information security risks which are in compliance with ISO 27001 standards.
-
Missing or Outdated Documentation: Procedures or records may be not updated or missing as per the latest ISO standards.
-
Inadequate Internal Audits: Poorly maintained internal audits which fail to cover the scope of ISMS may lead to major issues in future.
-
Lack of Employee Awareness and Training: Not training the employees and making them aware of their role in information security may cause severe problems.
-
Uncontrolled Access to Information Assets: Lack of access controls or weak user access reviews can result in unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Failure to Monitor and Measure ISMS Performance: Missing Key performance indicators (KPIs) or monitoring mechanisms which are not aligned with ISMS standards.
Impact Of Non-Conformity On The Organization
-
Delayed ISO 27001 Certification - Achieving certification can be a bigger challenge with major non-conformities.
-
Increase in Security Risks - Issues such as unauthorised access and data breaches may occur due to lack of resolution.
-
Loss of Customer and Stakeholder Trust: If the organization is not able to manage the information securely then partners and clients may not trust the organization.
-
Legal and Regulatory Penalties: Legal action or fines can be taken if the organization is found to be non-compliance with the rules and regulations.
-
Damage to Reputation: The organization may lose its reputation and credibility if there are repeated non-conformities found.
-
Increased Costs: Handling issues after escalation may cause increased expenses to the business.
-
Missed Business Opportunities: Organization may lose contracts and partnerships if they fail to get certified.
Impact of Non-Conformity On The Organization
The impact of non-conformities on an organization can be significant and far-reaching. When non-conformities are identified through an audit process, they can have various implications for the organization's operations, reputation, and overall success.
Here are some key impacts of non-conformities:
1. Operational Efficiency: Non-conformities can hinder the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization's processes and procedures. They can result in errors, delays, and wasted resources, ultimately affecting the organization's ability to deliver products or services to customers. Organizations can improve operational efficiency and reduce potential disruptions by addressing and rectifying non-conformities.
2. Customer Satisfaction: Non-conformities can directly impact customer satisfaction. An organization failing to meet established standards or requirements can result in product or service defects, quality issues, or delivery delays. This can lead to dissatisfied customers, negative reviews, and a damaged reputation. Organizations can enhance customer satisfaction and maintain a positive image in the market by ensuring compliance and resolving non-conformities.
3. Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Non-conformities can result in non-compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and industry standards. This can expose the organization to legal and financial risks, including fines, penalties, and lawsuits. Non-compliance can also lead to losing licenses, certifications, or permits necessary to operate within certain industries. By addressing non-conformities promptly and effectively, organizations can ensure compliance and mitigate legal and regulatory risks.
4. Cost Implications: Non-conformities can have financial implications for an organization. The costs of addressing and rectifying non-conformities, such as conducting investigations, implementing corrective actions, and re-training employees, can be substantial. Non-conformities can also result in financial losses due to customer dissatisfaction, decreased productivity, or reputational damage. Organizations can minimise costs and protect their financial stability by proactively investing in preventive measures and addressing non-conformities.
5. Continuous Improvement: Non-conformities present opportunities for improvement and growth. By analyzing the root causes and underlying issues behind non-conformities, organizations can identify areas for enhancement and implement corrective actions. This promotes a culture of continuous improvement, innovation, and learning within the organization. Organizations can strengthen their processes, systems, and performance by effectively managing non-conformities.
Non-conformities can significantly impact an organization's operations, reputation, and success. Organizations can promptly and effectively address non-conformities and improve operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, legal compliance, financial stability, and overall performance. Organizations can strive for continuous improvement and maintain a competitive edge in the market through a proactive approach to managing non-conformities.
Monitoring and Follow-up Measures
Monitoring and follow-up measures are essential components of addressing non-conformities within an organization. Once non-conformities have been identified through an audit process, it is crucial to establish a system for monitoring their resolution and implementing follow-up measures.
This ensures that the necessary corrective actions are taken and that the organization can effectively address the identified issues.
1. Monitoring Progress: After identifying non-conformities, it is important to establish monitoring mechanisms to track the progress of corrective actions. This may involve assigning responsible individuals or teams to oversee the implementation of the necessary changes. Regular updates and progress reports should be obtained to execute corrective actions effectively.
2. Reviewing Effectiveness: It is necessary to periodically review the effectiveness of the corrective actions taken to address the non-conformities. This may involve conducting follow-up audits or assessments to evaluate whether the identified issues have been adequately resolved. By reviewing the effectiveness of the corrective actions, organizations can ensure that the necessary improvements have been made and that the non-conformities have been effectively addressed.
3. Preventive Measures: Besides addressing the identified non-conformities, it is important to implement preventive measures to mitigate the risk of similar non-conformities occurring in the future. This may involve revising policies, procedures, or training programs to enhance compliance and prevent recurrence. By implementing preventive measures, organizations can proactively minimize the likelihood of non-conformities and enhance their overall compliance.
4. Documentation and Records: Throughout the monitoring and follow-up process, it is essential to maintain documentation and records of the corrective actions taken. This includes documenting the details of the non-conformities, the steps taken to address them, and any supporting evidence or documentation. These records indicate the organization's commitment to resolving non-conformities and can be valuable in demonstrating compliance during future audits or assessments.
5. Continuous Improvement: Monitoring and follow-up measures should be incorporated into the organization's overall continuous improvement process. The insights gained from addressing non-conformities can be used to identify areas for enhancement and drive ongoing improvements. By continually monitoring and following up on non-conformities, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement and ensure compliance remains a priority.
Monitoring and follow-up measures are crucial in addressing non-conformities within an organization. Organizations can effectively address non-conformities and enhance their overall compliance and performance by establishing monitoring mechanisms, reviewing effectiveness, implementing preventive measures, maintaining documentation, and driving continuous improvement.
Conclusion
The audit non-conformity report is essential for organizations to address and resolve identified issues. By implementing monitoring and follow-up measures, organizations can ensure that corrective actions are effectively executed and that non-conformities are adequately resolved.

