ISO 27001 Audit Calendar Template
Introduction
An audit calendar plays a crucial role in ensuring the smooth and efficient execution of audit processes within an organization. It serves as a tool to help auditors plan and schedule their activities, allocate resources effectively, and meet compliance requirements.
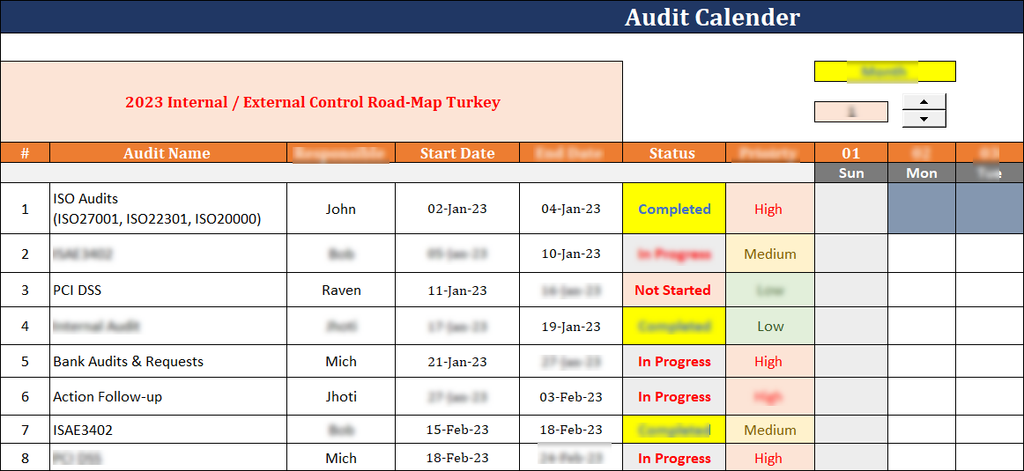
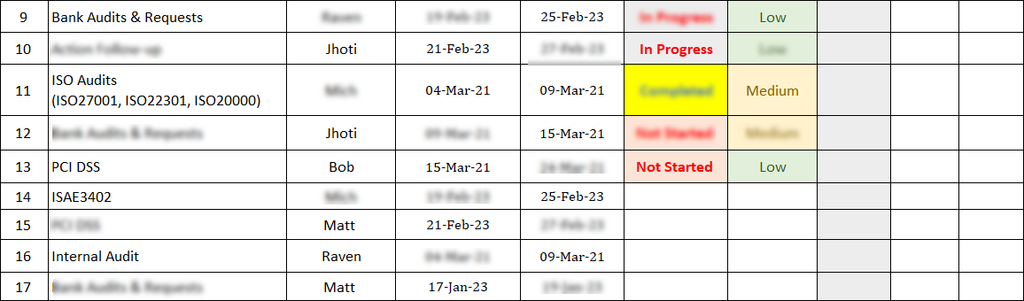
Overview
The ISO 27001:2022 Audit Calendar Template serves as a vital tool for organizations that seek to make effective implementation, monitoring, maintenance, and progressive improvement of their Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) compliant with the latest ISO/IEC 27001:2022 standard. This template is actually a strategic planning document, which thus enables the scheduling, coordination, and management of audits in a structured and proactive way.
It is Designed to support continual improvement and ensure ongoing compliance, the audit calendar will facilitate risk-based thinking, accountability, and traceability throughout the audit lifecycle.
Key Elements of an ISO 27001:2022 Audit Calendar Template
- ISO 27001 Audit Schedule
The calendar provides a complete time-frame during which audits are scheduled each year and includes:
-
- Internal audits aimed at verifying ISMS effectiveness.
- External audits, for example certification or surveillance.
- Surprise audits or unannounced reviews.
- Management reviews.
- Internal audits aimed at verifying ISMS effectiveness.
The regularity in scheduling all such audits makes audit systematic, timely, and a part of the organizational processes as per the requirements of Clause 9.2 of ISO/IEC 27001:2022.
- Audit Types
This template organizes different kinds of audits that have their own specific scopes and focuses. These include:
-
- Compliance audits (to verify adherence to ISO 27001 and internal regulations).
- Risk-based audits (to assess high-risk areas).
- Process and performance audits (to measure effectiveness and KPIs of controls).
- Compliance audits (to verify adherence to ISO 27001 and internal regulations).
Classifying audit types, therefore, enables organizations to appropriately allocate resources and set audit objectives accordingly.
- Roles and Responsibilities
Clear definition of responsibilities facilitates coordination and acknowledgment for the same. The template defines roles as:
-
- Lead Auditors, who plan and report
- Department Heads, who prepare for audits and take corrective actions
- Information Security Officers, who monitor compliance
- Top Management, who review and approve
- Lead Auditors, who plan and report
Defining responsibilities ensures the audit is done efficiently and in accordance with ISO 27001 leadership and planning requirements.
- Audit Criteria
Here are frameworks and policies that would serve as reference in the audit, such as:
-
- Clauses and Annex A controls of ISO/IEC 27001:2022
- Organizational ISMS policies and procedures
- Legal, regulatory, and contractual requirements
- Clauses and Annex A controls of ISO/IEC 27001:2022
The criteria for the audit bring consistency, objectivity, and agreement on both internal and external expectations.
- Auditor Qualifications
Requires documentation in place to assess auditor competency through the calendar comprising tracking for:
-
- Auditor certifications such as ISO 27001 Lead Auditor
- Experience and technical knowledge
- Programs attended for training or refresher courses
- Auditor certifications such as ISO 27001 Lead Auditor
This ensures the maintenance of accredited auditors as the requirement on ISO competency under Clause 7.2.
- Follow-Up and Corrective Actions
The template integrates tracking mechanisms for:
-
- Audit findings and observations
- Assigned corrective actions
- Due dates and verification methodologies
- Resolution status (open, in progress, closed)
- Audit findings and observations
This ensures a systematic approach to an address of Clause 10.1 (nonconformity and corrective action), facilitating continual improvement.
- Review and Revision Program
The template incorporates pre-defined review timeframes (quarterly or annually) to assure the audit calendar remains appropriate and up to date with respect to the changes in operational activities that reflect any changes due to:
-
- Changes within the business operations or scope
- Updates to regulation
- Trends of nonconformance or findings from audits
- Changes within the business operations or scope
Top 10 Benefits of Using an ISO 27001:2022 Audit Calendar Template
Organizations could benefit immensely by using an ISO 27001:2022 Audit Calendar Template while setting up or improving its information security management systems (ISMS). Several benefits are:
- Organized Approach: While applying the template audit calendar, it ensures a well-organized structure for planning and performing audits sufficient to warrant systematic evaluation of all aspects dealing with ISMS.
- Perfect Compliance: The life cycle of iso 27001 certification audit planning and scheduling processes ensures that organization requirement utilization on audit schedule template is measured against stakeholder regulation.
- Resource Management: All audit requirements like human personnel and materials are listed against each audit under an audit calendar and hence ensure proper allocation of resources so that there is minimum chance of assignment being missed.
- Timely Identification of Anomalies: Regular audits enable the organization to promptly identify potential problems that could involve either security cracks or non-conformities and take corrective measures to avoid upcoming hazards.
- Establishes Continuous Improvement: Continuous usage of an audit calendar will help organizations trace and monitor the audit finding for continuous adjustments in their processes.
- Accountability: Open calendar ensures accountability from all those team members who did actually take part in the audit process. Since everyone knows his/her duties and deadlines, establishing the culture of accountability becomes easy.
- Enhanced Communication: The audit calendar informs all stakeholders, thereby encouraging collaborative relationships and staying transparent on audit findings and subsequent actions.
- Standardization: Using a template becomes mandatory for all audits to be conducted in a standardized manner, resulting in uniform evaluation of the ISMS across departments or sites within an organization.
- Documentation and Reporting: A good documentation tool, as it provides convenient compiling of reports, tracking of changes over time, and providing evidence on the degree of conformance to external assessment.
- Cost-Saving: Audit conducted regularly can save the organization money over consideration for breaches or compliance failures while ultimately leading to its successfully running.
To sum it all up, the adoption of this kind of template will assist an organization in rendering its Information Security Management System highly efficient in ensuring continual improvement and duplicating commendable security practices.
Common Problems Raised by ISO27001 Audit and Solutions
-
Managerial Involvement
- A setback: Efforts towards compliance go off-course and become mismanaged in the absence of true top management involvement.
- Solution: Bring top management in at the very beginning and illustrate how really important ISO 27001 is to the business case for success. Keep them engaged by way of continued update briefings and meetings.
- A setback: Efforts towards compliance go off-course and become mismanaged in the absence of true top management involvement.
-
Bad Documentation
- A problem: The lack of appropriate documentation may hinder the auditing process.
- Solutions: Have all policies, procedures and controls documented and a regular review keep them current.
-
Employee Awareness and Training:
- Challenge: Employees do not know what is expected of them in an overall sense when it comes to information security.
- Solution: Raising awareness and conducting training programs for employees regularly on familiarizing them with the information security policies and procedures of ISO 27001.
- Challenge: Employees do not know what is expected of them in an overall sense when it comes to information security.
-
Scope Definition Problems
- Challenge: ISMS (Information Security Management System) scopes are a bit tricky.
- Solution: Involve the most important stakeholders in defining and documenting scope accurately so that it meets business objectives and lists important assets.
- Challenge: ISMS (Information Security Management System) scopes are a bit tricky.
-
Lack of Compliance with Controls
- Challenge: There are chances of divergence on compliance with information-security control measures.
- Solution: Conduct internal audits and assessments periodically to determine the current state of compliance with corrective relevancy.
- Challenge: There are chances of divergence on compliance with information-security control measures.
-
Qualification of Auditor
- Challenge: The auditors seem to have little or no relevant knowledge and/or competencies with regard to the importance of a given industry.
- Solution: Train and make use of auditors with experience in your industry, or employ certified third-party auditors with an impressive history.
- Challenge: The auditors seem to have little or no relevant knowledge and/or competencies with regard to the importance of a given industry.
-
Digital Transformation Challenges
- Challenge: Instant new technologies tend to get in one's way during the collective effort towards compliance.
- Solutions: Keep abreast of the trends and include ISMS-related projects in the initial phases of the digital initiatives to achieve compliance.
- Challenge: Instant new technologies tend to get in one's way during the collective effort towards compliance.
-
Manage Third Party Risks
- A problem: Risks brought into an organization via third-party vendors are often difficult to monitor.
- Solution: Institute a risk management program about vendor relationships by undertaking recurring assessments and attaching relevant security requirements to the third-party tie-up.
- A problem: Risks brought into an organization via third-party vendors are often difficult to monitor.
-
Report on the Necessity of Continual Improvement
- Challenges: Keeping an eye on compliance is an ongoing task.
- Solution: Nurturing a culture of continual improvement through periodic reviews and updates of processes within ISMS, factoring in feedback from audits and assessments.
- Challenges: Keeping an eye on compliance is an ongoing task.
ISO 27001 Audit Calendar Use: Best Practices for Design and Maintenance
Designing an ISO 27001 audit calendar is an asset for the organization that strives hard to comply with information security management standards. The best practices for having such an audit calendar include:
-
Clear Objectives Defined: Audit objectives shall be clarified before giving concrete details to the audit program to work into the calendar. Most likely, the following will be included as objectives:
- Compliancy per the ISO 27001:2022 clauses and controls in Annex A
-
Monitoring of risk treatment plans' effectiveness
- Identifying nonconformities and opportunities for improvement
- Preparation for external audits and recertification assessments
- Identifying nonconformities and opportunities for improvement
- Compliancy per the ISO 27001:2022 clauses and controls in Annex A
Defined audit objectives will stipulate the audit scope, frequency, and resources against strategic priorities.
-
Frequency Audit: The frequency audit specifies that ISMS audits shall be performed at planned intervals. The specific intervals and their application in different aspects of the audit have not been prescribed. Thus, audit frequency must also consider:
- Risk concentration, focusing on the high-risk or known weaknesses more frequently
- Past audit results, nonconformities, and trends of incidents sustained in between audits
- Changes within the Organization, for instance, opening new business units, releasing a new tool, or a new service
- Risk concentration, focusing on the high-risk or known weaknesses more frequently
Business-critical processes or high-risk IT environments would require quarterly audits while the low-risk functions may be reviewed annually.
-
Bring in Stakeholders: Planning of audits is solely the work of the audit department involved; every other department must be included so that audit scope misses no area. This should include:
- Departmental heads so as to scope the work-flows and documentation practices.
- Risk owners and control implementers of insights on mitigation status.
- Teams from Legal, Compliance, and HR for Audits Governed by Regulation.
- Departmental heads so as to scope the work-flows and documentation practices.
Stakeholder participation turns it into transparent events and helps spot those hidden crack cases or neglected areas.
-
Full Audit Criteria: Set criteria for audits very sensibly and objectively does involve:
- Mapping criteria directly to clauses and controls of ISO 27001
- Linkages established to internal security policies, procedures, and performance indicators
- Benchmarked against any known industry standards or against historical performance of audits
- Mapping criteria directly to clauses and controls of ISO 27001
Amidst the above would help any auditors at a similar compliance measurement, cut through with an understanding of departmental expectations.
-
Schedule Audits Long in Advance: The provisional dates for each audit and review sessions should be referred to in a rolling 12-month calendar. This may include:
- Internal audits.
- External certification and surveillance audits.
- Timelines for management review A calendar in this manner gives enough advance notice to allow preparation of evidence and resources. If possible embed the calendar into your QMS or ISMS tool.
- Internal audits.
-
Allocate Resources: There should be enough people to work effectively with the help of appropriate tools. Thus, the following should be included in the design of this program:
- Internal auditors, trained and certified, with no conflict of interest.
- Schedules of auditor as well as auditee blocked for the time.
-
Budget for external audit services made available when required.
- Tools/templates are made available for planning, checklists, reporting, and follow-ups.
- Internal auditors, trained and certified, with no conflict of interest.
Among the most important risks of neglecting resource planning is demotivation, which may delay the timely offsetting of findings.
-
Flexibility: Audit Calendar will define a schedule how it should, however, be flexible enough to change audits if sometime due to unexpected events:
-
Cyber-attacks, mergers, change of leadership
- Ad-hoc or trigger audits have already been or will be scheduled with the emergence of new threats
- Ad-hoc or trigger audits have already been or will be scheduled with the emergence of new threats
- Same can be adjusted for audit findings or internal controls failing
-
Cyber-attacks, mergers, change of leadership
Such agility keeps ISMS awake to the risks that are real and the priorities.
- Pre-audit briefing exercise: Just have a pre-audit meeting organized before the audit. A pre-audit briefing would clarify:
-
- Scope, time frame, checklist
- Assurance that all evidence required is up to date and accessible
-
Maintain confidentiality, objectivity, and ensure roles for team members
- Logistics, timing of interviews, access to systems, and arrangements of the working area.
- Scope, time frame, checklist
By adopting these best practices, organizations shall boast a robust ISO 27001 audit calendar which will translate into enhanced compliance, better security, and continual improvement.
Conclusion
The process of designing and maintaining an audit calendar for ISO 27001 requires the establishment of key measures that shall ensure the efficacy of your information security management system; producing ahead of time plans of audits in consideration of business goals or scheduling the regular reviews. When setting such a calendar, it would be best if a template was utilized and perhaps to source some assignments and schedule service auditing ISO 27001 certification. Get organized and be proactive about your audits.

