ISO 22301 Clause 6.2 Business Continuity Objectives and Planning
Definition of Business Continuity Objectives
Business Continuity Objectives (BCOs) refer to the specific goals and targets that an organization sets to ensure the continuity of critical business functions during and after a disruptive incident.
BCOs provide a clear understanding of what the organization wants to achieve during a disruptive incident and how it will measure success. BCOs should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) to ensure that they are realistic and achievable.
Importance of Business Continuity Objectives
Business Continuity Objectives are critical because they help organizations to prioritize their activities during a disruptive incident. By setting clear and measurable objectives, organizations can ensure that they are taking the necessary steps to protect their critical business functions.
BCOs help organizations to stay focused on their key priorities and avoid distractions that may arise during a disruptive incident. Additionally, BCOs provide a basis for monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of the organization's business continuity management system.
Key Elements of Business Continuity Objectives
The key elements of Business Continuity Objectives include:
1. Specificity: BCOs should be clear and specific, with a focus on critical business functions and activities.
2. Measurability: BCOs should be measurable, with clear targets and metrics that can be used to monitor progress and measure success.
3. Achievability: BCOs should be achievable, with a focus on realistic and practical objectives that the organization can accomplish.
4. Relevance: BCOs should be relevant, with a focus on the critical business functions that are essential for the organization's survival and success.
5. Time-bound: BCOs should be time-bound, with clear deadlines and timelines for achieving the objectives. This ensures that the organization is taking timely action to protect critical business functions during a disruptive incident.
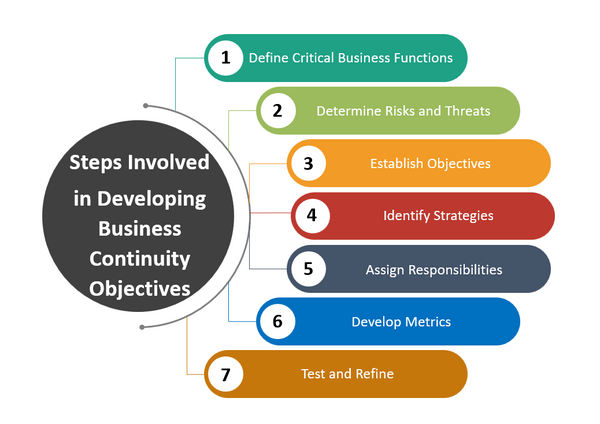
Steps Involved in Developing Business Continuity Objectives
Developing effective Business Continuity Objectives (BCOs) requires careful planning and consideration.
Here are some steps involved in developing BCOs:
1.Define Critical Business Functions: Identify the critical business functions that the organization needs to protect during a disruptive incident. These are the core activities that are essential for the organization's survival and success.By following these steps, organizations can develop clear and effective BCOs that prioritize the protection of critical business functions during a disruptive incident.
Planning for Business Continuity
Planning for business continuity involves developing a comprehensive plan for how an organization will ensure the continuity of critical business functions during and after a disruptive incident.
This plan should include a business impact analysis, a business continuity plan, recovery time objectives, emergency response procedures, and regular testing and review.
By taking these steps, organizations can prioritize their activities and resources during a disruptive incident and minimize the impact on their critical business functions, ensuring the long-term success of the organization.
Implementing Business Continuity Objectives and Plans
Implementing Business Continuity Objectives (BCOs) and Plans involves putting the developed strategies and plans into action.
Here are some key steps involved in implementing BCOs and plans:
1. Communicate the Plan: Communicate the BCOs and the Business Continuity Plan (BCP) to all employees, stakeholders, and other relevant parties. Ensure that they understand their roles and responsibilities during a disruptive incident and are aware of the procedures for communicating during and after a disruptive incident.
2. Implement Business Continuity Strategies: Implement the strategies developed to achieve the BCOs. This may involve setting up alternate locations, establishing redundant systems, and ensuring that employees have the necessary tools and resources to work remotely.
3. Train Employees: Train employees on their roles and responsibilities during a disruptive incident. This includes training on emergency response procedures, communication protocols, and recovery strategies.
4. Monitor Progress: Monitor progress towards achieving the BCOs and ensuring the continuity of critical business functions. This includes regularly reviewing the BCP and adjusting it as necessary to ensure that it remains effective.
5. Test the Plan: Regularly test the BCP to ensure that it is effective and up-to-date. This includes conducting simulated disruptive incidents and reviewing and updating the plan as necessary.
6. Evaluate Performance: Evaluate the performance of the BCP and the effectiveness of the BCOs in achieving the organization's objectives. Identify areas for improvement and make adjustments to the plan as necessary.
By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement their BCOs and BCP, ensuring the continuity of critical business functions during and after a disruptive incident. This helps to minimize the impact of disruptive incidents and ensures the long-term success of the organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, developing and implementing Business Continuity Objectives and Plans are critical steps for organizations to ensure the continuity of their critical business functions during and after disruptive incidents. By prioritizing their activities and resources, organizations can minimize the impact of disruptive incidents and ensure their long-term success.

