ISO 22301 : Incident Response Structure
ISO 22301 is an internationally recognized standard that lays the foundation for establishing a robust incident response structure within an organization. This standard is designed to help businesses and institutions prepare for, respond to, and recover from disruptive incidents effectively.
By providing a structured framework, ISO 22301 ensures that organizations can identify potential risks, develop comprehensive incident response plans, and implement proactive measures to mitigate the impact of unexpected events. This standard not only safeguards an organization's reputation and operations but also bolsters its resilience, helping it adapt and thrive in the face of adversity. ISO 22301 is a valuable tool for ensuring business continuity in an increasingly uncertain world.
Importance of ISO 22301:Legal and Regulatory Registry
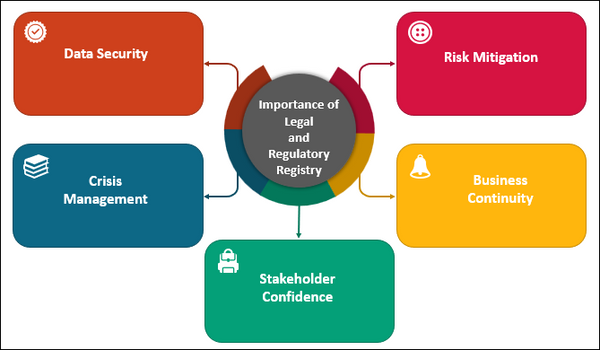
- Compliance Assurance: A Legal and Regulatory Registry helps organizations stay compliant with a myriad of laws and regulations applicable to their industry. This ensures that the organization avoids legal pitfalls and penalties associated with non-compliance, which can be detrimental to business operations.
- Risk Mitigation: By maintaining an up-to-date registry, organizations can identify potential legal and regulatory risks in advance. This proactive approach allows for the development of strategies to mitigate these risks and protect the organization from legal disputes or financial liabilities.
- Business Continuity: ISO 22301 is all about ensuring business continuity, and legal compliance is a crucial aspect of this. A Legal and Regulatory Registry aids in understanding how various legal requirements might impact an organization during incidents and helps in crafting response and recovery plans that take these factors into account.
- Documentation and Evidence: In the event of an incident, having a well-maintained registry provides documented evidence of the organization's commitment to compliance. This can be valuable in legal proceedings and in demonstrating a commitment to responsible corporate governance.
- Stakeholder Confidence: Maintaining legal and regulatory compliance fosters trust among stakeholders, including customers, investors, and partners. It demonstrates the organization's commitment to ethical and responsible business practices, which can enhance its reputation and relationships within the industry.
- Global Operations: For organizations with a global presence, a Legal and Regulatory Registry is invaluable for managing compliance across multiple jurisdictions. It helps in navigating the complex landscape of international laws and regulations.
- Adaptation to Change: Laws and regulations are subject to change, and organizations need to adapt quickly. A registry makes it easier to stay informed about legal updates and adjust policies and practices accordingly, ensuring that the organization remains in compliance.
- Data Security: In cases where data protection laws are involved, such as GDPR or HIPAA, maintaining a registry of data-related regulations is critical for safeguarding sensitive information and avoiding data breaches.
- Competitive Advantage: Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements can also be a source of competitive advantage. Organizations that can demonstrate their adherence to these standards often have an edge in the market, as it can be a selling point for customers who prioritize secure and ethical business partners.
- Crisis Management: During incidents or crises, having a Legal and Regulatory Registry in place streamlines decision-making by providing clear guidelines for handling legal aspects, ensuring that the organization responds appropriately to legal challenges that may arise.
Key elements of ISO 22301:Legal and Regulatory Registry
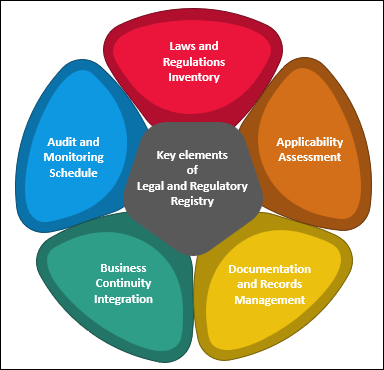
- Laws and Regulations Inventory: Create a comprehensive inventory of all relevant laws and regulations that apply to the organization. This should cover international, national, regional, and local regulations as applicable.
- Applicability Assessment: Clearly define how each law or regulation is applicable to the organization. This might include specifying the departments, processes, or products to which each law pertains.
- Compliance Requirements: Specify the specific compliance requirements for each law and regulation. This should encompass key obligations, deadlines, reporting requirements, and penalties for non-compliance.
- Updates and Changes: Establish a system for monitoring and tracking updates and changes to laws and regulations. This includes identifying authoritative sources and ensuring that the registry is regularly updated.
- Responsibilities and Accountabilities: Clearly outline who within the organization is responsible for ensuring compliance with each law and regulation. This should include designating compliance officers or teams.
- Compliance Records: Maintain a record of compliance activities, including documentation of steps taken to meet regulatory requirements, audits, and assessments conducted, and any remediation efforts in case of non-compliance.
- Reporting Mechanisms: Define the reporting mechanisms for legal and regulatory compliance. This might include internal reporting structures, incident reporting procedures, and external reporting to regulatory authorities.
- Incident Response Plans: Develop incident response plans specific to legal and regulatory issues. These plans should outline procedures for addressing non-compliance, reporting incidents, and rectifying violations.
- Training and Awareness: Implement training programs to ensure that employees are aware of and understand the legal and regulatory requirements relevant to their roles. Regular training can help prevent non-compliance.
- Documentation and Records Management: Establish a system for the organized storage and retrieval of all legal and regulatory documents, including compliance records, notices, permits, and licenses.
- Third-Party Compliance: If the organization engages with third parties, such as suppliers or partners, ensure that they also comply with relevant laws and regulations. Include a mechanism for assessing and monitoring third-party compliance.
- Business Continuity Integration: Integrate legal and regulatory compliance considerations into the organization's broader business continuity and incident response plans. Ensure that legal and regulatory requirements are addressed during incident response and recovery efforts.
- Audit and Monitoring Schedule: Develop a schedule for regular audits and monitoring of legal and regulatory compliance. This should include internal audits as well as any external assessments or inspections.
- Continuous Improvement: Foster a culture of continuous improvement in legal and regulatory compliance. Encourage the organization to learn from past incidents or violations and make necessary adjustments to prevent reoccurrence.
The Benefits of ISO 22301:Legal and Regulatory Registry
- Enhanced Compliance: Adherence to Legal Obligations: Maintaining a Legal and Regulatory Registry ensures that an organization remains in full compliance with relevant laws and regulations. This reduces the risk of legal penalties and reputational damage associated with non-compliance.
- Risk Mitigation: Proactive Risk Identification: The registry facilitates the identification of potential legal and regulatory risks, enabling organizations to take proactive measures to mitigate these risks and protect themselves from legal disputes and financial liabilities.
- Improved Business Continuity: Resilience in the Face of Legal Challenges: Legal and regulatory compliance is a fundamental aspect of business continuity. The registry helps in crafting response and recovery plans that account for the legal dimensions of incidents, ensuring smoother operations during disruptions.
- Documentation and Accountability: Clear Documentation: The registry provides documented evidence of the organization's commitment to compliance. In the event of legal proceedings, it serves as proof of responsible corporate governance, which can be instrumental in protecting the organization's interests.
- Stakeholder Trust: Enhanced Reputation: Maintaining compliance fosters trust among stakeholders, including customers, investors, and partners. It demonstrates the organization's commitment to ethical and responsible business practices, enhancing its reputation and credibility.
- Global Operations Management: Effective International Compliance: For organizations with global operations, the registry simplifies the management of compliance across multiple jurisdictions. It aids in navigating the complex landscape of international laws and regulations.
- Competitive Advantage: Market Edge: Compliance with legal and regulatory requirements can provide a competitive advantage. Organizations that can demonstrate adherence to these standards often have an edge in the market, attracting customers who prioritize secure and ethical business partners.
- Crisis Management: Efficient Legal Handling during Incidents: Having a Legal and Regulatory Registry in place streamlines decision-making during incidents, ensuring that the organization responds appropriately to legal challenges that may arise.
- Adaptation to Change: Timely Response to Legal Updates: As laws and regulations change, the registry keeps the organization informed, allowing for timely adjustments in policies and practices to maintain compliance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the implementation of an ISO 22301-compliant Legal and Regulatory Registry is not just a compliance requirement but a strategic imperative for modern organizations. Such a registry not only ensures legal compliance but also acts as a pillar of resilience, risk management, and competitive advantage. It provides a structured approach to identify, assess, and address legal and regulatory obligations, safeguarding an organization from legal pitfalls and financial liabilities.
Beyond this, it fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement in compliance practices. Moreover, the Legal and Regulatory Registry aligns seamlessly with the broader goals of ISO 22301, enhancing an organization's overall business continuity and incident response capabilities. In an era of evolving legal landscapes and heightened scrutiny, a well-maintained registry is an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to thrive amidst challenges and build trust with stakeholders while minimizing legal and regulatory risks.